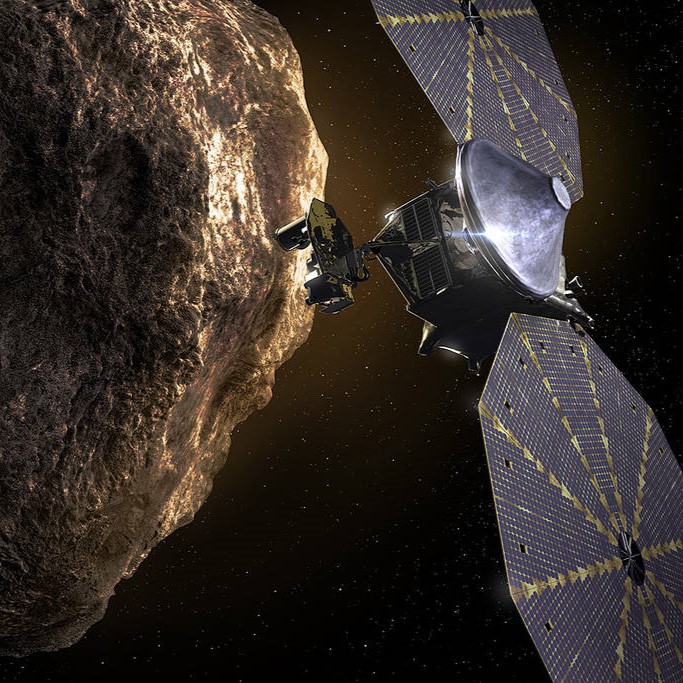

NASA's Lucy spacecraft is in the midst of three Earth flybys that ultimately will fling it to the main asteroid belt and Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids . In October 2022, a year after the spacecraft’s launch, Lucy made its first flyby of Earth .
On November 1, 2023, Lucy will swing past the still-unnamed (152830) 1999 VD57. To get there, engineers will begin a series of small maneuvers in May 2023. As a bonus, the detour allows scientists to conduct an engineering test of the spacecraft's asteroid-tracking navigation system.
The Lucy mission will take a 40,000-mile detour to visit this asteroid

NASA has added a tenth asteroid flyby to the record-breaking Lucy mission — and this one will serve as a dress rehearsal for a tool that could forever change how we study space rocks.
The Lucy mission: In October 2021, NASA launched Lucy, its first mission to the Trojan asteroids, a group of asteroids that follow Jupiter’s orbit around the sun.
NASA's Record-Breaking Lucy Spacecraft Has a New Asteroid Target
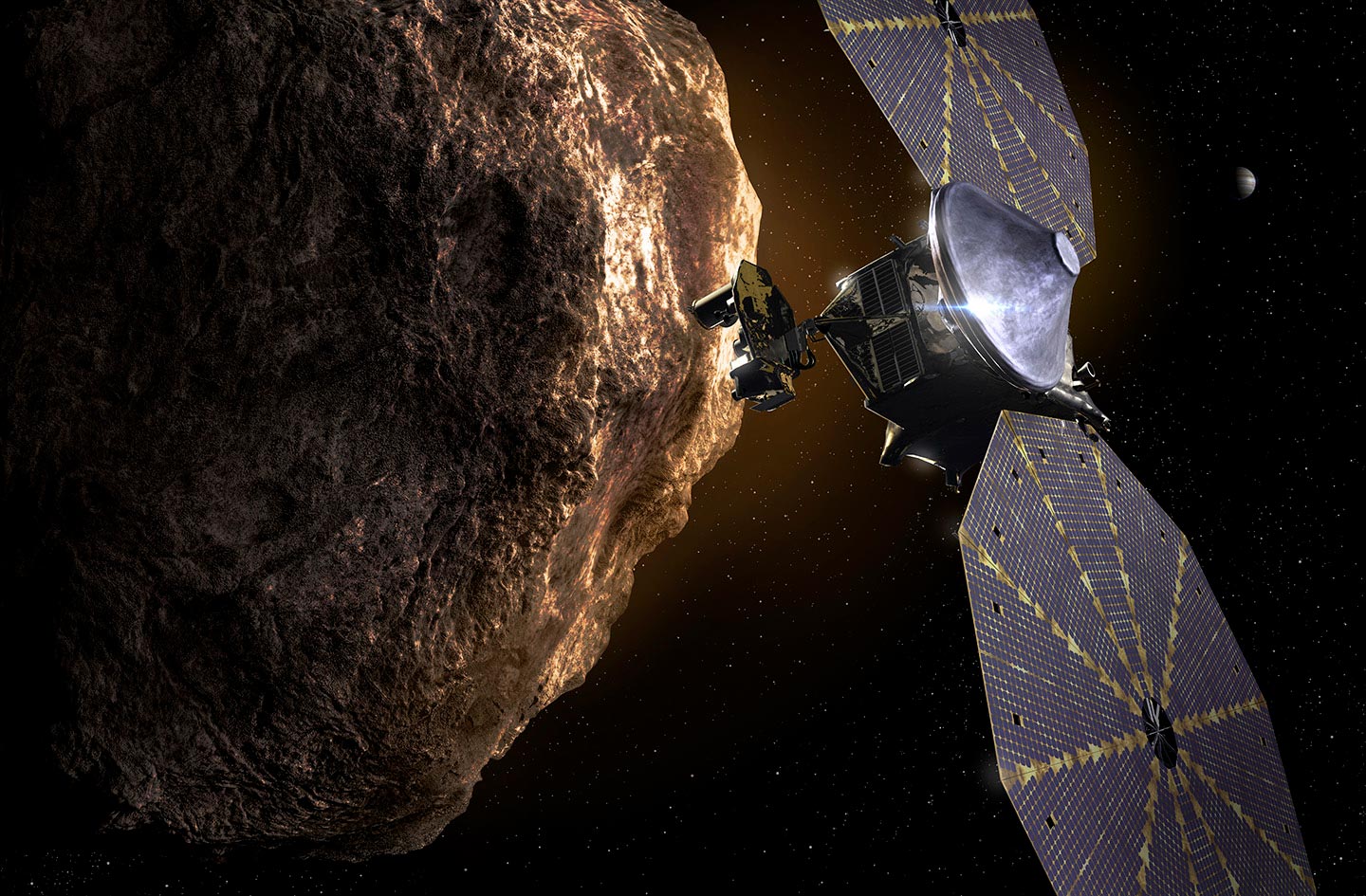

By Southwest Research Institute January 30, 2023 Artist's concept of NASA's Lucy spacecraft at an asteroid. Credit: NASA
The Lucy team realized that, by adding a small maneuver, the spacecraft would be able to get an even closer look at this asteroid. So, on January 24, the team officially added it to Lucy's tour as an engineering test of the spacecraft's pioneering terminal tracking system.
Webb Space Telescope finds water ice in rings of an asteroid

Cosmos » Space » James Webb Space Telescope finds water ice in rings of an asteroid
NASA's James Webb Space telescope has found water ice in the ring of a distant object in our solar system, but it's not Saturn with its remarkable rings, or Neptune, Uranus or even Jupiter which has rings which are too faint to be seen by most telescopes.
Asteroid mining startup AstroForge to launch first missions this year - SpaceNews
WASHINGTON — A startup with plans to mine asteroids for metals says it will launch its first two missions this year, including one that will fly by a near Earth asteroid.
AstroForge announced Jan. 24 that it will launch a cubesat into low Earth orbit in April to test its refinery technologies.
Rubble pile asteroid is 4.2 billion years old and nearly indestructible
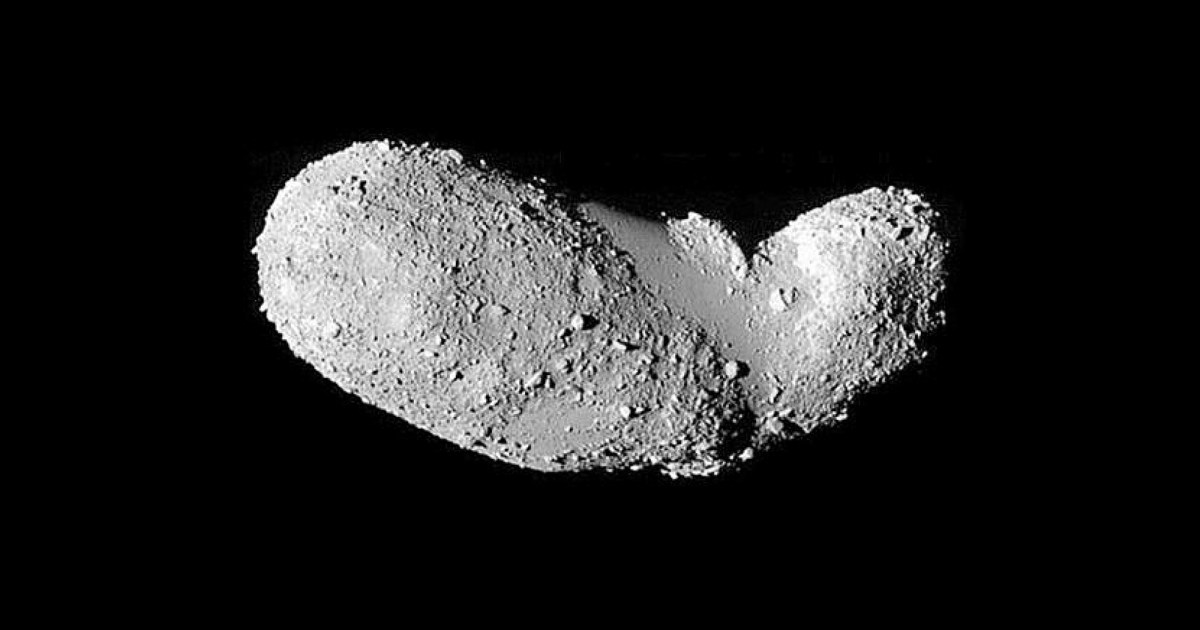

Based on just three particles of dust, Australian researchers have determined that a near-Earth asteroid is 4.2 billion years old — and practically indestructible.
The knowledge gap: Asteroids can broadly be divided into two types: monolithic (one big rock) or rubble pile (many rocks held together by gravity).
Army of the Alien Monkeys
Earth is nice. We want it.
We welcome your submission to us.
No comments:
Post a Comment